2015 Bladder Cancer Review
Bladder Cancer Statistics
The American Cancer Society's estimates for bladder cancer prevalence in the United States for 2016 are:
- About 76,960 new cases of bladder cancer (about 58,950 in men and 18,010 in women)
- About 16,390 deaths from bladder cancer (about 11,820 in men and 4,570 in women)
Bladder cancer occurs when cells in the lining of the bladder grow uncontrollably and form tumor thickening of normal tissues, which can eventually spread to other parts of the body.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
The most common symptom noted is blood in the urine which is identified in 80% of bladder cancer patients. Other symptoms are similar to UTI (urinary traction infection) which include irritation when urinating, urgency, and frequency of urination. In advanced cases of bladder cancer, the tumor can actually block either the entrance and/or exit of urine to and from the bladder and this can lead to symptoms of severe flank pain, infection, and damage to the kidneys.
Risks Factors for Bladder Cancer
- Smoking is the most important risk factor for bladder cancer. Smokers are at least 3 times as likely to get bladder cancer as nonsmokers. Smoking causes about half of all bladder cancers in both men and women.
- Carcinogens in the environment (if worked in the rubber, chemical, leather industries, hairdressers, machinists, metal workers, painters, textile workers and firefighters).
- Caucasians have two times higher risk than African Americans, but the disease tends to be more aggressive at time of presentation in African Americans.
MSLC Bladder Cancer Study
Unfortunately, even though bladder cancer is common, the general population has very little knowledge about it. Here at Montefiore St. Luke’s Cornwall (MSLC), in order to shed light and bring awareness of this disease to our local population, we have performed a retrospective study to evaluate how bladder cancer diagnosis/treatment in our population compares to national trends.
Objective:
Diagnosis, treatment and outcomes of bladder cancer at MSLC were compared to NCDB (National Cancer Data Base) in 2014. In addition, we reviewed the adherence of treatment modalities to NCCN (the National Comprehensive Cancer Network) guidelines. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network is a nonprofit alliance of 26 cancer centers throughout the United States. They develop clinical practice guidelines in Oncology, designed to help health care professionals diagnose, treat, and manage cancer patient care.
Data collected from MSLC vs NCDB
Incidence of Bladder Cancer: 2014 MSLC vs. 2013 New York State and
2013 National Cancer Data Base (NCDB)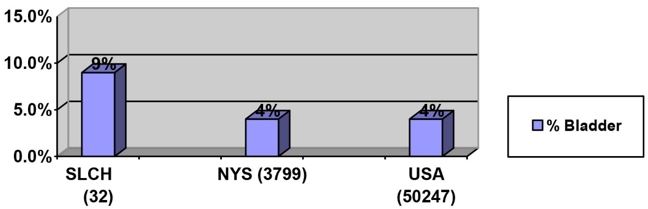
In 2014, 32 patients were diagnosed with bladder cancer at MSLC, representing 9% of all newly diagnosed cancer at the hospital. This case incidence is compared to both the New York State and NCDB bladder cancer at 4%.
Age at Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Incidence %
2014 MSLC vs. 2013 National Cancer Data Base (NCDB)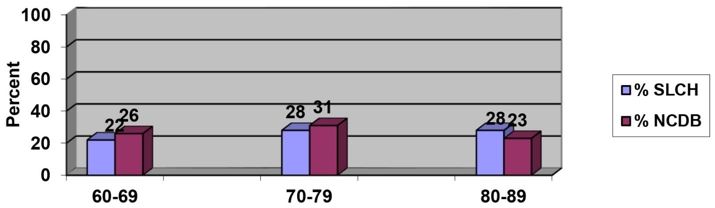
Age at Diagnosis: MSLC has a similar patient population to that reported by the National Cancer Database.
- age group 60-69: 22% for MSLC compared to 26% for NCDB
- age group 70-79 : 28% for MSLC compared to 31% for NCDB
- age group 80-89 : 28% for MSLC compared to 23% for NCDB
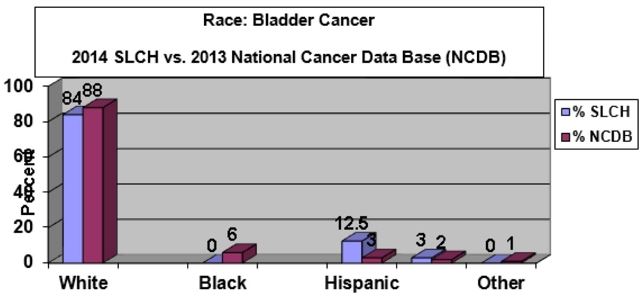
Race The data above represents the race that the patients "self identified"
upon registration. We had a higher percentage of Hispanic patients than
that reported in the NCDB. This is not unusual given the patient population
in our community.
- Caucasian: 84% for MSLC vs 88% for NCDB
- Hispanic: 12% for MSLC vs 3 % for NCDB
- African Americans: 0 % for MSLC vs 6% for NCDB
Gender: Bladder Cancer
2014 MSLC vs. 2013 National Cancer Data Base (NCDB)
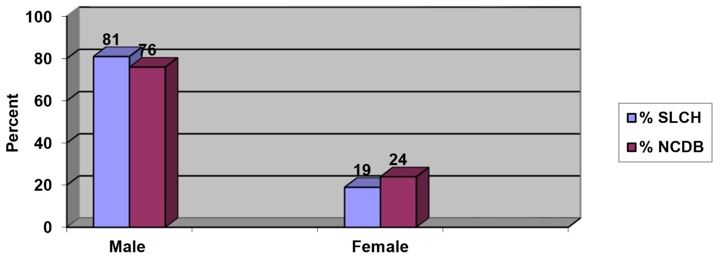 Roughly 80% men compared to 20% women at MSLC, which is very similar to
that reported in the NCDB.
Roughly 80% men compared to 20% women at MSLC, which is very similar to
that reported in the NCDB.
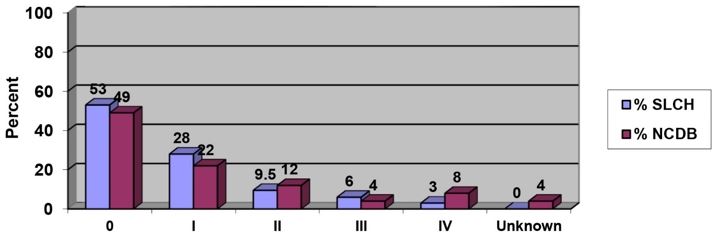
Stage at Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer
2014 MSLC vs. 2013 National Cancer Data Base (NCDB)
The majority of patients are seen in early stage (Stage 0) which accounts
for 53% at MSLC during 2014 and 49% for 2013 NCDB cases. All 32 patients
(100%) were staged by undergoing upper tract imaging with either CT Scan
or renal ultrasound, followed by cystoscopic evaluation (looking into
the bladder with a scope) and endoscopic bladder resection (bladder surgery).
Treatment
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) has established guidelines in managing bladder cancer. According to the NCCN guidelines all high-grade Stage 0a, Stage 0cis, and Stage I should be offered intravesical immunotherapy(BCG) after endoscopic bladder resection. Fifteen out of thirty-two patients were identified as having high grade bladder eligible for immunotherapy. Fourteen of the fifteen eligible patients received intravesical BCG, as outlined by the NCCN guidelines. One patient did not receive immunotherapy which appears to be surgeon's preference in this particular patient. This demonstrates a 93% compliance to the guidelines.
Treatment for muscle invasive bladder cancer includes removal of the bladder (cystectomy) or chemotherapy with simultaneous radiation therapy. Six patients were identified as having muscle invasive bladder cancer, Stages II – IV, in 2014 at MSLC. Treatment for five of the six patients were managed according to NCCN guidelines, a compliance rate of 83%, by having their bladders removed. The sixth patient completed radiation therapy after their course of chemotherapy.
Ongoing Surveillance:
The second step in managing superficial bladder cancer is monitoring for recurrence. All 32 patients (100% compliance) demonstrated follow-up for their continued cancer care at MSLC.
Summary
In general, the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of bladder cancer at MSLC and NCDB were relatively similar. One area of discrepancy is the incidence of bladder cancer in our Hispanic population. The demographics of the City of Newburgh demonstrate a Hispanic population comprising nearly 50% of the total population. But, only 12% of patients diagnosed with bladder cancer were Hispanic. We need to ensure that this community is aware of the link between smoking and bladder cancer, and the importance of early screening.
One of our objectives at MSLC is to collect and analyze information on the cancer patients diagnosed and/or treated at MSLC, and to compare our population data to that of other national community hospitals. We strive to ensure that all cancer patients receiving care at MSLC have access to quality standards and achieve the best possible outcomes. This study demonstrates that our clinicians are providing care within national guidelines.
Jaspreet Singh, DO
Montefiore St. Luke’s Cornwall
Department of Surgery, Division of Urology
Cancer Committee Physician Liaison
Presented at Cancer Committee 12/3/2015
Montefiore St. Luke’s Cornwall, Oncology Data
4th Floor Main
70 Dubois Street
Newburgh, NY 12550

 Pay My Bill
Pay My Bill
 Contact Us
Contact Us
 Patient Portal
Patient Portal
 Donate
Donate